Tocotrienols for Brain Health and Cognitive Support

Introduction
Vitamin E is an essential fat-soluble vitamin that is important in maintaining certain health functions such as reproduction, skin health and brain protection. Vitamin E exists naturally in eight forms (d-alpha-, d-beta-, d-gamma-, and d-delta-tocopherol and d-alpha-, d-beta-, d-gamma-, and d-delta-tocotrienol). Among these vitamin E, tocotrienols’ unique biological activity in relation to brain protection and cognitive health have attracted tremendous interests from both academic, research scientists as well as dietary supplement companies.
The Journey Began from an Nih-funded in Vitro Study of Vitamin E Isomers in Neuron Cell Survival
While both tocopherols and tocotrienols are Vitamin E and have similar molecular structures, they differ in term of the unsaturation in their tail (side chain). Tocotrienol has three unsaturated bonds in its isoprenoid tail; whereas tocopherol has a fully saturated tail.
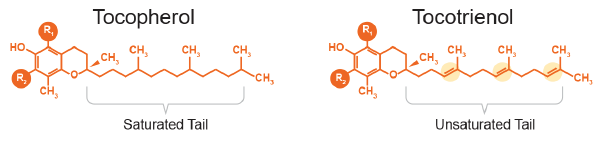
While both tocopherols and tocotrienols are Vitamin E and have similar molecular structures, they differ in term of the unsaturation in their tail (side chain). Tocotrienol has three unsaturated bonds in its isoprenoid tail; whereas tocopherol has a fully saturated tail.
In a layman’s term, tocotrienols can be defined as the “Unsaturated Form of Vitamin E”.
Tocotrienols are a lipid-soluble antioxidant. Its antioxidant activity was reported to be 40 to 60 times more potent than the regular vitamin E tocopherol, by the late Dr. Lester Packer, one of the world’s foremost antioxidant research scientists. In late 90s, his then student (Dr. Chandan K. Sen) carried out a blinded study on vitamin E isomers (tocopherols and tocotrienols) and their response to glutamate challenge in protecting the brain. Interestingly, tocotrienols significantly out-performs tocopherol where only nano-molar (10-9) concentration of tocotrienol is required in rescuing neuron cells from glutamate-induced brain damages. On the other hand – approximately 1000 times higher concentration of tocopherol is required to achieve the same level of protection. This discovery leads to the beginning of tocotrienol’s research in neuro protection and cognitive health.
Subsequently, over the past 20 years with funding from NIH, Prof. Sen and his research team at the Ohio State University Medical Center published five different mechanisms in which tocotrienols modulate molecular signals that lead to protection of neuronal cells from stroke- or glutamate-induced injuries:
Neuroprotection of Palm Tocotrienol Complex
60% of human brain is made up of fat and with its high oxygen consumption, the brain is highly susceptible to oxidative stress. A team of Japanese researchers from Department of Neurology, Okayama University, assessed the therapeutic and anti-inflammatory effects of pretreatment with palm tocotrienols/tocopherol complex on transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAO) in mice. These mice were fed with palm tocotrienols/tocopherol complex (200mg/kg/day) for 1 month prior to the challenge of tMCAO. The treated group reported significant neuroprotective effects against oxidative stress via anti-apoptotic/autophagic cell death as well as by anti-inflammatory effects in ischemic mice brain.
In another study – Prof Sen published another study which shows that supplementation with palm tocotrienol complex improves blood flow to the brain in a canine model, by enhancing leptomeningeal collateralization to the middle cerebral artery territory and increased expression of arteriogenic genes (chloride intracellular channel 1 and TIMP 1).
A two-year, randomized, controlled trial with follow up of white matter lesion (WML) change in human subjects was conducted by researchers from the University Science Malaysia. It was one of the largest human clinical trials on palm tocotrienol complex that looked at White Matter Lesions induced by TIA (transient ischemic attack). The results were published in American Heart Association’s journal – Stroke which shows that natural full spectrum palm tocotrienols/tocopherol complex attenuates the progression of brain white matter lesion load in human, which are linked to reduced risk of neurodegenerative cognitive diseases and stroke.
Tocotrienols and Cognitive Health/Cognitive Decline
Brain is undoubtedly a remarkable organ with important functional responsibilities such as reading, learning, balance, sleep, memory, behavior, movement, vision, appetite, emotion and etc.
Chronic alcohol intake is known to induce brain dysfunction and neuronal damage. The cognitive-supporting effects of tocotrienols and alpha-tocopherol was assessed in Male Wistar rats, given ethanol (10g/kg) for 10 weeks. Administration of tocotrienol showed a more pronounced effects in preventing the change of biochemical, molecule (i.e. oxidative-nitrosative stress, TNF-alpha and IL-1beta levels) and behavior (i.e. learning and memory) in the brains of ethanol-challenged rats. Hence, tocotrienol has more potent potency in addressing cognitive deficits associated with chronic alcohol consumption.
Brain-aging is another reason of cognitive decline (i.e. memory or thinking skills) and even leading to a more serious issue – “dementia”. The improvement of learning and memory deficit by supplementation of palm tocotrienols/tocopherol complex were reported in 2 recent papers by researchers from Malaysia and Japan. The Malaysian researchers discovered that aged rats supplemented with palm tocotrienols/tocopherol complex (200mg/kg/day) for 3 months shows a markedly reduction level of anxiety, improved spatial learning and memory, reduced amount and severity of DNA damage, a reduced level of MDA, as well as increased levels of antioxidant enzyme activity and plasma/brain vitamin E compared with age-matched controls. Meantime, the Japanese researchers found that tocotrienols can reach the brain even though with oxidatively-damaged blood brain barrier in the aged rats and markedly improves age-related deficits in learning and memory.
In 2020, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study reported the cognitive function improvement through supplementation of palm tocotrienol complex and astaxanthin in adults who felt a memory decline. The study involved 44 healthy subjects who received either a combination of astaxanthin (9mg) and tocotrienol (50mg) or a placebo capsule daily, for 12 weeks supplementation. The astaxanthin-tocotrienols group shows a significant improvement in composite memory and verbal memory in Cognitrax at the end of the intervention period.
Vitamin E Tocotrienols / Tocopherol in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Ad
Researchers at the Aging Research Center, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm studied the relationship of vitamin E – both tocopherols and tocotrienols and Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) and Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) in cross-sectional multicenter study of older European population. MCI is often thought as the precursor of AD. The study population was derived from the AddNeuroMed Project, a multicenter European longitudinal study on the detection of biomarkers for AD. It is one of the largest cohorts of AD and MCI subjects, gathered from more than 6 European countries. A total of 4 published epidemiological studies show that all vitamin E isoforms (d-mixed tocopherols and d-mixed tocotrienols) are important to support a healthy cognitive function, rather than to regular vitamin E alpha-tocopherol alone. In addition, low plasma tocopherols and tocotrienols levels, especially tocotrienols, are associated with increased odds of MCI and AD. Meanwhile, elevated levels of tocopherol and tocotrienol forms are associated with reduced risk of cognitive impairment in older adults. The fourth publication, published in Experimental Gerontology, suggests plasma level of tocopherols and tocotrienols play potential role of nutritional biomarkers as indirect indicators of AD pathology, and connecting tocotrienols to improved cognitive health/reduced MCI risk.
Conclusion
Tocotrienols, more known as the “Super Vitamin E” – has a significant body of science and human studies on brain health/neuroprotection benefits and cognitive improvement. They play an important role in protecting the brain and supporting healthy cognitive functions, when challenged by external toxins and due to the inevitable aging process. Hence, when formulating a formula for brain health or cognitive support, it is prudent to incorporate the right form of vitamin E – ie: Tocotrienols.
Tocotrienols for Brain Health and Cognitive Support

Introduction
Vitamin E is an essential fat-soluble vitamin that is important in maintaining certain health functions such as reproduction, skin health and brain protection. Vitamin E exists naturally in eight forms (d-alpha-, d-beta-, d-gamma-, and d-delta-tocopherol and d-alpha-, d-beta-, d-gamma-, and d-delta-tocotrienol). Among these vitamin E, tocotrienols’ unique biological activity in relation to brain protection and cognitive health have attracted tremendous interests from both academic, research scientists as well as dietary supplement companies.
The Journey Began from an Nih-funded in Vitro Study of Vitamin E Isomers in Neuron Cell Survival
While both tocopherols and tocotrienols are Vitamin E and have similar molecular structures, they differ in term of the unsaturation in their tail (side chain). Tocotrienol has three unsaturated bonds in its isoprenoid tail; whereas tocopherol has a fully saturated tail.

While both tocopherols and tocotrienols are Vitamin E and have similar molecular structures, they differ in term of the unsaturation in their tail (side chain). Tocotrienol has three unsaturated bonds in its isoprenoid tail; whereas tocopherol has a fully saturated tail.
In a layman’s term, tocotrienols can be defined as the “Unsaturated Form of Vitamin E”.
Tocotrienols are a lipid-soluble antioxidant. Its antioxidant activity was reported to be 40 to 60 times more potent than the regular vitamin E tocopherol, by the late Dr. Lester Packer, one of the world’s foremost antioxidant research scientists. In late 90s, his then student (Dr. Chandan K. Sen) carried out a blinded study on vitamin E isomers (tocopherols and tocotrienols) and their response to glutamate challenge in protecting the brain. Interestingly, tocotrienols significantly out-performs tocopherol where only nano-molar (10-9) concentration of tocotrienol is required in rescuing neuron cells from glutamate-induced brain damages. On the other hand – approximately 1000 times higher concentration of tocopherol is required to achieve the same level of protection. This discovery leads to the beginning of tocotrienol’s research in neuro protection and cognitive health.
Subsequently, over the past 20 years with funding from NIH, Prof. Sen and his research team at the Ohio State University Medical Center published five different mechanisms in which tocotrienols modulate molecular signals that lead to protection of neuronal cells from stroke- or glutamate-induced injuries:
Neuroprotection of Palm Tocotrienol Complex
60% of human brain is made up of fat and with its high oxygen consumption, the brain is highly susceptible to oxidative stress. A team of Japanese researchers from Department of Neurology, Okayama University, assessed the therapeutic and anti-inflammatory effects of pretreatment with palm tocotrienols/tocopherol complex on transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAO) in mice. These mice were fed with palm tocotrienols/tocopherol complex (200mg/kg/day) for 1 month prior to the challenge of tMCAO. The treated group reported significant neuroprotective effects against oxidative stress via anti-apoptotic/autophagic cell death as well as by anti-inflammatory effects in ischemic mice brain.
In another study – Prof Sen published another study which shows that supplementation with palm tocotrienol complex improves blood flow to the brain in a canine model, by enhancing leptomeningeal collateralization to the middle cerebral artery territory and increased expression of arteriogenic genes (chloride intracellular channel 1 and TIMP 1).
A two-year, randomized, controlled trial with follow up of white matter lesion (WML) change in human subjects was conducted by researchers from the University Science Malaysia. It was one of the largest human clinical trials on palm tocotrienol complex that looked at White Matter Lesions induced by TIA (transient ischemic attack). The results were published in American Heart Association’s journal – Stroke which shows that natural full spectrum palm tocotrienols/tocopherol complex attenuates the progression of brain white matter lesion load in human, which are linked to reduced risk of neurodegenerative cognitive diseases and stroke.
Tocotrienols and Cognitive Health/Cognitive Decline
Brain is undoubtedly a remarkable organ with important functional responsibilities such as reading, learning, balance, sleep, memory, behavior, movement, vision, appetite, emotion and etc.
Chronic alcohol intake is known to induce brain dysfunction and neuronal damage. The cognitive-supporting effects of tocotrienols and alpha-tocopherol was assessed in Male Wistar rats, given ethanol (10g/kg) for 10 weeks. Administration of tocotrienol showed a more pronounced effects in preventing the change of biochemical, molecule (i.e. oxidative-nitrosative stress, TNF-alpha and IL-1beta levels) and behavior (i.e. learning and memory) in the brains of ethanol-challenged rats. Hence, tocotrienol has more potent potency in addressing cognitive deficits associated with chronic alcohol consumption.
Brain-aging is another reason of cognitive decline (i.e. memory or thinking skills) and even leading to a more serious issue – “dementia”. The improvement of learning and memory deficit by supplementation of palm tocotrienols/tocopherol complex were reported in 2 recent papers by researchers from Malaysia and Japan. The Malaysian researchers discovered that aged rats supplemented with palm tocotrienols/tocopherol complex (200mg/kg/day) for 3 months shows a markedly reduction level of anxiety, improved spatial learning and memory, reduced amount and severity of DNA damage, a reduced level of MDA, as well as increased levels of antioxidant enzyme activity and plasma/brain vitamin E compared with age-matched controls. Meantime, the Japanese researchers found that tocotrienols can reach the brain even though with oxidatively-damaged blood brain barrier in the aged rats and markedly improves age-related deficits in learning and memory.
In 2020, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study reported the cognitive function improvement through supplementation of palm tocotrienol complex and astaxanthin in adults who felt a memory decline. The study involved 44 healthy subjects who received either a combination of astaxanthin (9mg) and tocotrienol (50mg) or a placebo capsule daily, for 12 weeks supplementation. The astaxanthin-tocotrienols group shows a significant improvement in composite memory and verbal memory in Cognitrax at the end of the intervention period.
Vitamin E Tocotrienols / Tocopherol in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Ad
Researchers at the Aging Research Center, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm studied the relationship of vitamin E – both tocopherols and tocotrienols and Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) and Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) in cross-sectional multicenter study of older European population. MCI is often thought as the precursor of AD. The study population was derived from the AddNeuroMed Project, a multicenter European longitudinal study on the detection of biomarkers for AD. It is one of the largest cohorts of AD and MCI subjects, gathered from more than 6 European countries. A total of 4 published epidemiological studies show that all vitamin E isoforms (d-mixed tocopherols and d-mixed tocotrienols) are important to support a healthy cognitive function, rather than to regular vitamin E alpha-tocopherol alone. In addition, low plasma tocopherols and tocotrienols levels, especially tocotrienols, are associated with increased odds of MCI and AD. Meanwhile, elevated levels of tocopherol and tocotrienol forms are associated with reduced risk of cognitive impairment in older adults. The fourth publication, published in Experimental Gerontology, suggests plasma level of tocopherols and tocotrienols play potential role of nutritional biomarkers as indirect indicators of AD pathology, and connecting tocotrienols to improved cognitive health/reduced MCI risk.
Conclusion
Tocotrienols, more known as the “Super Vitamin E” – has a significant body of science and human studies on brain health/neuroprotection benefits and cognitive improvement. They play an important role in protecting the brain and supporting healthy cognitive functions, when challenged by external toxins and due to the inevitable aging process. Hence, when formulating a formula for brain health or cognitive support, it is prudent to incorporate the right form of vitamin E – ie: Tocotrienols.
Tocotrienols for Brain Health and Cognitive Support

Introduction
Vitamin E is an essential fat-soluble vitamin that is important in maintaining certain health functions such as reproduction, skin health and brain protection. Vitamin E exists naturally in eight forms (d-alpha-, d-beta-, d-gamma-, and d-delta-tocopherol and d-alpha-, d-beta-, d-gamma-, and d-delta-tocotrienol). Among these vitamin E, tocotrienols’ unique biological activity in relation to brain protection and cognitive health have attracted tremendous interests from both academic, research scientists as well as dietary supplement companies.
The Journey Began from an Nih-funded in Vitro Study of Vitamin E Isomers in Neuron Cell Survival
While both tocopherols and tocotrienols are Vitamin E and have similar molecular structures, they differ in term of the unsaturation in their tail (side chain). Tocotrienol has three unsaturated bonds in its isoprenoid tail; whereas tocopherol has a fully saturated tail.

While both tocopherols and tocotrienols are Vitamin E and have similar molecular structures, they differ in term of the unsaturation in their tail (side chain). Tocotrienol has three unsaturated bonds in its isoprenoid tail; whereas tocopherol has a fully saturated tail.
In a layman’s term, tocotrienols can be defined as the “Unsaturated Form of Vitamin E”.
Tocotrienols are a lipid-soluble antioxidant. Its antioxidant activity was reported to be 40 to 60 times more potent than the regular vitamin E tocopherol, by the late Dr. Lester Packer, one of the world’s foremost antioxidant research scientists. In late 90s, his then student (Dr. Chandan K. Sen) carried out a blinded study on vitamin E isomers (tocopherols and tocotrienols) and their response to glutamate challenge in protecting the brain. Interestingly, tocotrienols significantly out-performs tocopherol where only nano-molar (10-9) concentration of tocotrienol is required in rescuing neuron cells from glutamate-induced brain damages. On the other hand – approximately 1000 times higher concentration of tocopherol is required to achieve the same level of protection. This discovery leads to the beginning of tocotrienol’s research in neuro protection and cognitive health.
Subsequently, over the past 20 years with funding from NIH, Prof. Sen and his research team at the Ohio State University Medical Center published five different mechanisms in which tocotrienols modulate molecular signals that lead to protection of neuronal cells from stroke- or glutamate-induced injuries:
Neuroprotection of Palm Tocotrienol Complex
(200mg/kg/day) for 1 month prior to the challenge of tMCAO. The treated group reported significant neuroprotective effects against oxidative stress via anti-apoptotic/autophagic cell death as well as by anti-inflammatory effects in ischemic mice brain. In another study – Prof Sen published another study which shows that supplementation with palm tocotrienol complex improves blood flow to the brain in a canine model, by enhancing leptomeningeal collateralization to the middle cerebral artery territory and increased expression of arteriogenic genes (chloride intracellular channel 1 and TIMP 1). A two-year, randomized, controlled trial with follow up of white matter lesion (WML) change in human subjects was conducted by researchers from the University Science Malaysia. It was one of the largest human clinical trials on palm tocotrienol complex that looked at White Matter Lesions induced by TIA (transient ischemic attack). The results were published in American Heart Association’s journal – Stroke which shows that natural full spectrum palm tocotrienols/tocopherol complex attenuates the progression of brain white matter lesion load in human, which are linked to reduced risk of neurodegenerative cognitive diseases and stroke.
Tocotrienols and Cognitive Health/Cognitive Decline
Brain is undoubtedly a remarkable organ with important functional responsibilities such as reading, learning, balance, sleep, memory, behavior, movement, vision, appetite, emotion and etc.
Chronic alcohol intake is known to induce brain dysfunction and neuronal damage. The cognitive-supporting effects of tocotrienols and alpha-tocopherol was assessed in Male Wistar rats, given ethanol (10g/kg) for 10 weeks. Administration of tocotrienol showed a more pronounced effects in preventing the change of biochemical, molecule (i.e. oxidative-nitrosative stress, TNF-alpha and IL-1beta levels) and behavior (i.e. learning and memory) in the brains of ethanol-challenged rats. Hence, tocotrienol has more potent potency in addressing cognitive deficits associated with chronic alcohol consumption.
Brain-aging is another reason of cognitive decline (i.e. memory or thinking skills) and even leading to a more serious issue – “dementia”. The improvement of learning and memory deficit by supplementation of palm tocotrienols/tocopherol complex were reported in 2 recent papers by researchers from Malaysia and Japan. The Malaysian researchers discovered that aged rats supplemented with palm tocotrienols/tocopherol complex (200mg/kg/day) for 3 months shows a markedly reduction level of anxiety, improved spatial learning and memory, reduced amount and severity of DNA damage, a reduced level of MDA, as well as increased levels of antioxidant enzyme activity and plasma/brain vitamin E compared with age-matched controls. Meantime, the Japanese researchers found that tocotrienols can reach the brain even though with oxidatively-damaged blood brain barrier in the aged rats and markedly improves age-related deficits in learning and memory.
In 2020, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study reported the cognitive function improvement through supplementation of palm tocotrienol complex and astaxanthin in adults who felt a memory decline. The study involved 44 healthy subjects who received either a combination of astaxanthin (9mg) and tocotrienol (50mg) or a placebo capsule daily, for 12 weeks supplementation. The astaxanthin-tocotrienols group shows a significant improvement in composite memory and verbal memory in Cognitrax at the end of the intervention period.
Vitamin E Tocotrienols / Tocopherol in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Ad
Researchers at the Aging Research Center, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm studied the relationship of vitamin E – both tocopherols and tocotrienols and Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) and Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) in cross-sectional multicenter study of older European population. MCI is often thought as the precursor of AD. The study population was derived from the AddNeuroMed Project, a multicenter European longitudinal study on the detection of biomarkers for AD. It is one of the largest cohorts of AD and MCI subjects, gathered from more than 6 European countries. A total of 4 published epidemiological studies show that all vitamin E isoforms (d-mixed tocopherols and d-mixed tocotrienols) are important to support a healthy cognitive function, rather than to regular vitamin E alpha-tocopherol alone. In addition, low plasma tocopherols and tocotrienols levels, especially tocotrienols, are associated with increased odds of MCI and AD. Meanwhile, elevated levels of tocopherol and tocotrienol forms are associated with reduced risk of cognitive impairment in older adults. The fourth publication, published in Experimental Gerontology, suggests plasma level of tocopherols and tocotrienols play potential role of nutritional biomarkers as indirect indicators of AD pathology, and connecting tocotrienols to improved cognitive health/reduced MCI risk.
Conclusion
Tocotrienols, more known as the “Super Vitamin E” – has a significant body of science and human studies on brain health/neuroprotection benefits and cognitive improvement. They play an important role in protecting the brain and supporting healthy cognitive functions, when challenged by external toxins and due to the inevitable aging process. Hence, when formulating a formula for brain health or cognitive support, it is prudent to incorporate the right form of vitamin E – ie: Tocotrienols.





