Healthful Bioactives from Palm Fruits (An Educational Video)
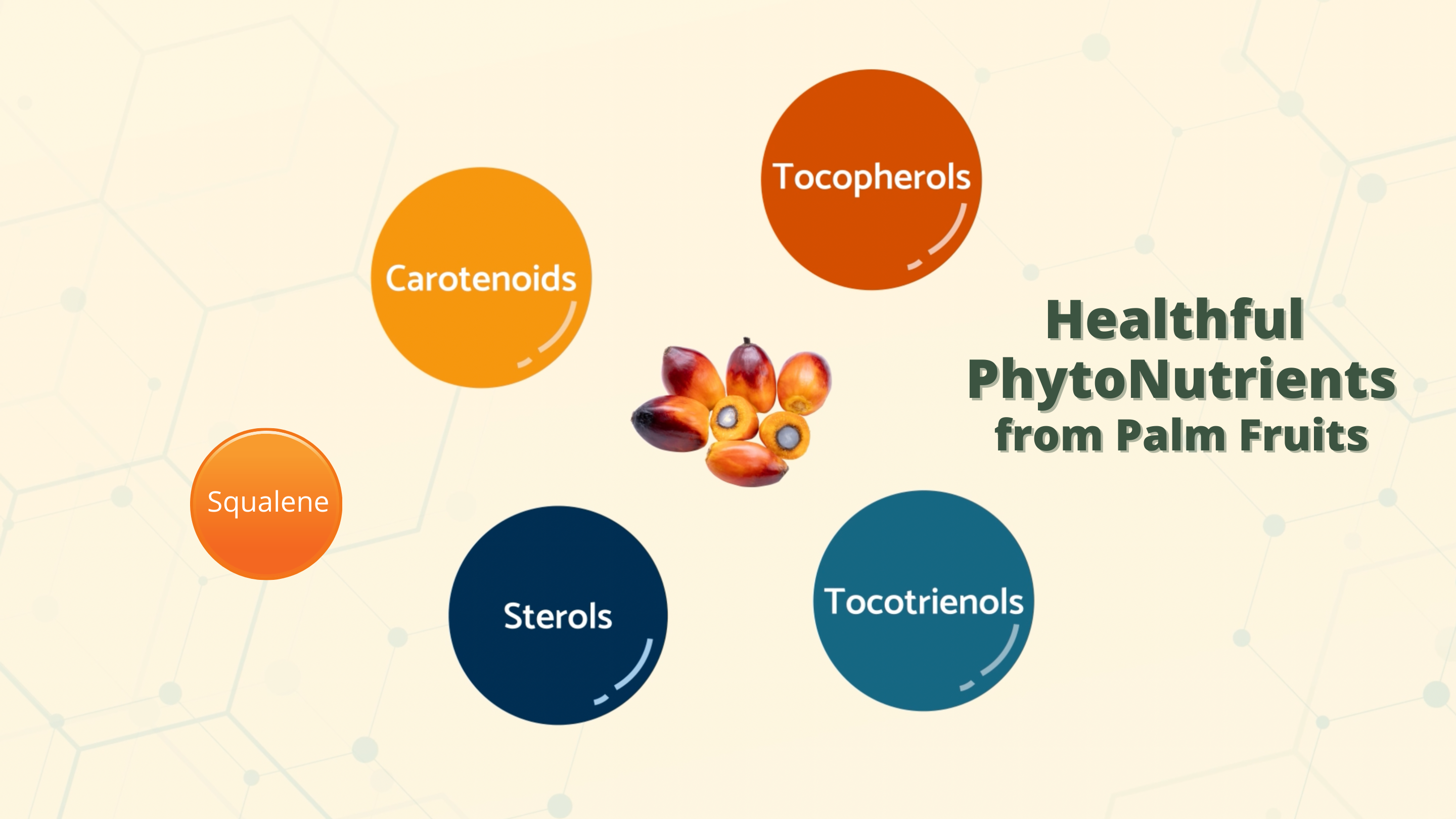
Palm Fruit or Red Palm Oil (Elaeis guineesis) is well endowed with a bouquet of phytonutrients beneficial to health, such as tocotrienols, carotenoids, phytosterols and squalene1&2.
Palm Fruit / Red Palm Oil has a rich orange-red colour due to its high content of natural mixed-carotenes (primarily alpha- and beta-carotene). In fact, it’s considered the richest source of natural mixed-carotene and provitamin A – approximately 15 times more mixed-carotene than carrot3.
Palm Fruit is also one of the richest natural sources of vitamin E and the best source of a potent form of vitamin E known as tocotrienol. There are two major forms of vitamin E – tocopherol and tocotrienol. Studies reported that tocotrienol is 40 – 60 times more potent than tocopherol as an antioxidant in preventing lipid-peroxidation4. Clinical studies have reported various health attributes of palm tocotrienols such as brain protection (i.e. attenuates the progression of white matter lesion)5, liver support (i.e. mitigate fatty liver (NAFLD))6, hair growth7 etc.
Besides tocotrienols and mixed-carotenes, palm fruits contain other health beneficial phytonutrients such as phytosterols, squalene and CoQ-10.
This video provides an overview of the Healthful Bioactive from Palm Fruits. Click here for the complete video – Healthful Bioactives from Palm Fruits.
References:
- Obahiagbon, F.I. et al. (2012). A review: Aspects of the African oil palm (Elaeis guineensis jacq.) and the implications of its bioactives in human health. American Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 3:106-119.
- Sundram, K. et al. (2003). Palm fruit chemistry and nutrition. Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 12:355-62.
- Rice, A.L. et al. (2010). Moving from efficacy to effectiveness: Red palm oil’s role in preventing vitamin A deficiency. The Journal of American College of Nutrition. 29:302S-313S.
- Serbinova, E. et al. (1991). Free radical reclying and intramembrane mobility in the antioxidant properties of alpha-tocopherol and alpha-tocotrienol.Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 10, 263-275.
- Gopalan, Y. et al. (2014). Clinical Investigation of the Protective Effects of Palm Vitamin E Tocotrienols on Brain White Matter Lesion. Stroke. 45(5), 1422-8.
- Magosso, E. et al. (2013). Tocotrienols for Normalisation of Hepatic Echogenic Response in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver: A Randomised Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Nutrition Journal. 12(1), 166.
- Beoy, L.A. et al. (2010). Effects of tocotrienol supplementation on hair growth in human volunteers.Tropical Life Sciences Research. 21(2):91-9.